Free Response Practice Question (with solution)- Interpreting River Data from Text Files
| <-- Back to Analyzing Student Names | Next to Analyzing Integers --> |
Interpreting River Data from Text Files
Write a Java program that reads the text file that contains the names of rivers and the country in which it flows, along with the estimated length of the river in miles. The program should do the following:
- Search and print all the rivers located in a country whose name is read from the user. Your program should print 'No rivers found', in case no river info is available for that country.
- Search and print the country to which a given river belongs to. Read the name of the river from the user. In case no river with that name exists in the file, your program should print an appropriate message.
- Calculate and print the names of the rivers which are more than 3500 miles long. The program should print appropriate message if no river(s) exist which are longer than the specified length.
- Find and print the names of the longest and shortest river. Assume no two rivers have the same length.
Sample Input: rivers.txt
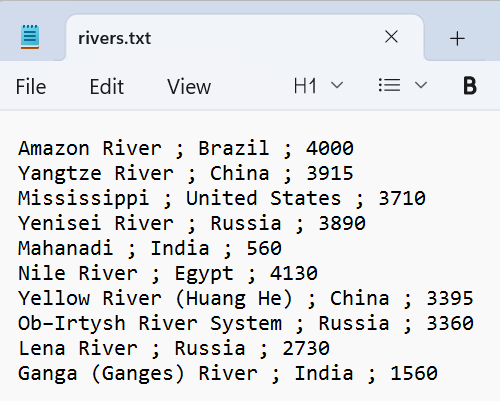
Note: The data presented here about rivers is hypothetical.
Also, note that the data is separated using semi colons.
Sample Output (a): Search and print all the rivers located in a country whose name is read from the user. Your program should print 'No rivers found', in case no river info is available for that country.
View Output

Solution for (a):
View SolutionRiversRunner.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RiversRunner {
public static void searchRivers(Scanner sc, String country) {
boolean found = false;
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
if (line.toLowerCase().indexOf(country.toLowerCase()) != -1) {
found = true;
System.out.println(line);
}
}
if (!found)
System.out.println("No river found in: " + country);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File inputFile = new File("rivers.txt");
Scanner input = new Scanner(inputFile);
System.out.println("Enter the name of the country whose rivers are to searched: ");
Scanner readCountry = new Scanner(System.in);
String country = readCountry.next();
searchRivers(input, country);
readCountry.close();
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("File not found: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Sample Output (b): Search and print the country to which a given river belongs to. Read the name of the river from the user. In case no river with that name exists in the file, your program should print an appropriate message.
View Output

Solution for (b):
View SolutionSearchCountryRiverRunner.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SearchCountryRiverRunner {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File inputFile = new File("rivers.txt");
Scanner input = new Scanner(inputFile);
System.out.println("Enter the name of the river: ");
Scanner readRiver = new Scanner(System.in);
String river = readRiver.next();
boolean found = false;
while (input.hasNext()) {
String line = input.nextLine();
if (line.toLowerCase().indexOf(river.toLowerCase()) != -1) {
found = true;
String[] arr = line.split(" ; ");
System.out.println("River: "+ arr[0] + ". It is found in: "+arr[1]);
}
}
if (!found)
System.out.println("No river found named: " + river);
readRiver.close();
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("File not found: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Sample Output (c): Calculate and print the names of the rivers which are more than 3500 miles long. The program should print appropriate message if no river(s) exist which are longer than the specified length.
View Output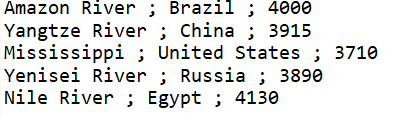
Solution for (c):
View SolutionLongerRiversRunner.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LongerRiversRunner {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File inputFile = new File("rivers.txt");
Scanner input = new Scanner(inputFile);
int length = 3500;
boolean found = false;
while (input.hasNext()) {
String line = input.nextLine();
String[] details = line.split(" ; ");
int len = Integer.parseInt(details[2].trim());
if (len >= length) {
found = true;
System.out.println(line);
}
}
if (!found)
System.out.println("No river found greater than: "+length+ " miles");
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("File not found: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Sample Output (d): Find and print the names of the longest and shortest river. Assume no two rivers have the same length.
View Output
Solution for (d):
View SolutionLongShortRiversRunner.java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LongShortRiversRunner {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File inputFile = new File("rivers.txt");
Scanner input = new Scanner(inputFile);
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // can also be initialized to 0 in this case
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // can also be initialized to 0 in this case
String riverLong = null;
String riverShort = null;
while (input.hasNext()) {
String line = input.nextLine();
String[] details = line.split(" ; ");
int len = Integer.parseInt(details[2].trim());
if (len > max) {
riverLong = details[0];
max = len;
}
if (len < min) {
riverShort = details[0];
min = len;
}
}
System.out.println("Longest River: " + riverLong + " || Length: " + max);
System.out.println("Shortest River: " + riverShort + " || Length: " + min);
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("File not found: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Java project files (with input files):
- rivers.txt
- RiversRunner.java
- SearchCountryRiverRunner.java
- LongerRiversRunner.java
- LongShortRiversRunner.java
| <-- Back to Analyzing Student Names | Next to Analyzing Integers --> |